Blockchain Technology Cryptocurrency Concept Can Use Stock …
Introduction: Why Blockchain Matters in Today’s Digital Economy
In an era where data drives decisions and trust is often in short supply, blockchain emerges as a foundational technology reshaping how we handle transactions, records, and value. Imagine a system where no single entity holds all the power, yet everything remains secure and transparent. That’s blockchain at its core.
This guide demystifies blockchain for newcomers, starting from Bitcoin’s origins and extending to altcoins like XRP. With the global cryptocurrency market capitalization hovering around $3 trillion as of December 2025, understanding these basics isn’t just academic—it’s essential for anyone eyeing the intersection of finance and technology. Whether you’re a curious investor or a financially literate reader, grasping these concepts can provide clarity amid the noise.
What Is Blockchain? A Simple Breakdown
Blockchain is essentially a decentralized digital ledger that records transactions across a network of computers. Unlike traditional databases controlled by a central authority, blockchain distributes copies of the ledger to all participants, making it tamper-resistant.
Think of it as a chain of blocks, where each block contains a list of transactions. Once added, a block can’t be altered without changing all subsequent blocks, which requires network consensus. This structure ensures immutability and security.
At its heart, blockchain solves the “double-spending” problem—preventing the same digital asset from being spent twice—without needing intermediaries like banks.
The Birth of Bitcoin: Blockchain’s First Application
Bitcoin, introduced in 2008 by the pseudonymous Satoshi Nakamoto, was the first practical use of blockchain. It functions as a peer-to-peer electronic cash system, often called “digital gold” due to its scarcity (capped at 21 million coins) and store-of-value properties.
Bitcoin’s blockchain uses a consensus mechanism called Proof of Work (PoW). Miners compete to solve complex mathematical puzzles, validating transactions and adding blocks. The winner receives newly minted bitcoins as a reward, incentivizing network security.
As of December 2025, Bitcoin’s price stands at approximately $88,000, reflecting its dominance in the market.

Bitcoin Price (BTC) Analysis: S&P 500 Takes the Lead in 2025
This chart illustrates Bitcoin’s historical price trends, showing its volatility and long-term growth.
Consensus Mechanisms: The Backbone of Blockchain Trust
Consensus mechanisms are protocols that ensure all nodes in a blockchain network agree on the ledger’s state. Without a central authority, these mechanisms prevent fraud and maintain integrity.
Proof of Work, as seen in Bitcoin, requires computational power to validate blocks. It’s secure but energy-intensive, consuming electricity comparable to a small country’s usage.
Proof of Stake (PoS), an alternative, selects validators based on the number of coins they hold and “stake” as collateral. Ethereum transitioned to PoS in 2022, reducing energy consumption by 99%. PoS is more efficient but raises concerns about wealth concentration.
Other mechanisms, like Delegated Proof of Stake or Proof of Authority, offer variations suited to different networks. Consensus is what makes blockchain decentralized and reliable.
Smart Contracts: Automating Agreements on the Blockchain
Smart contracts are self-executing programs stored on the blockchain that automatically enforce terms when conditions are met. Coined by Nick Szabo in the 1990s but popularized by Ethereum, they eliminate the need for intermediaries.
Picture a vending machine: Insert money, select an item, and it dispenses automatically. Smart contracts work similarly—code defines rules, and the blockchain executes them transparently.
For instance, in decentralized finance (DeFi), smart contracts handle lending without banks. They’re traceable, irreversible, and reduce costs, but bugs can lead to losses, as seen in historical exploits.

How Smart Contracts Work Infographic Stock Photo – Image of …
This infographic breaks down how smart contracts function, highlighting their key components.
Exploring Altcoins: From XRP to Diverse Use Cases
Altcoins are any cryptocurrencies besides Bitcoin, each addressing specific limitations or introducing new features. They leverage blockchain for varied applications.
XRP, created by Ripple Labs, focuses on cross-border payments. Unlike Bitcoin’s mining, XRP uses a consensus protocol where validators agree on transactions, enabling near-instant settlements at low costs. It’s designed for financial institutions, aiming to rival systems like SWIFT.
As of late 2025, XRP’s price chart shows resilience amid regulatory clarity, with market movements reflecting adoption in remittances.

The XRP’s Price Prediction From 2023 To 2030
Other altcoins include Ethereum for smart contracts and stablecoins like USDT for value stability.
Polkadot’s Parachain Auctions: Bridging Blockchains for Altcoins
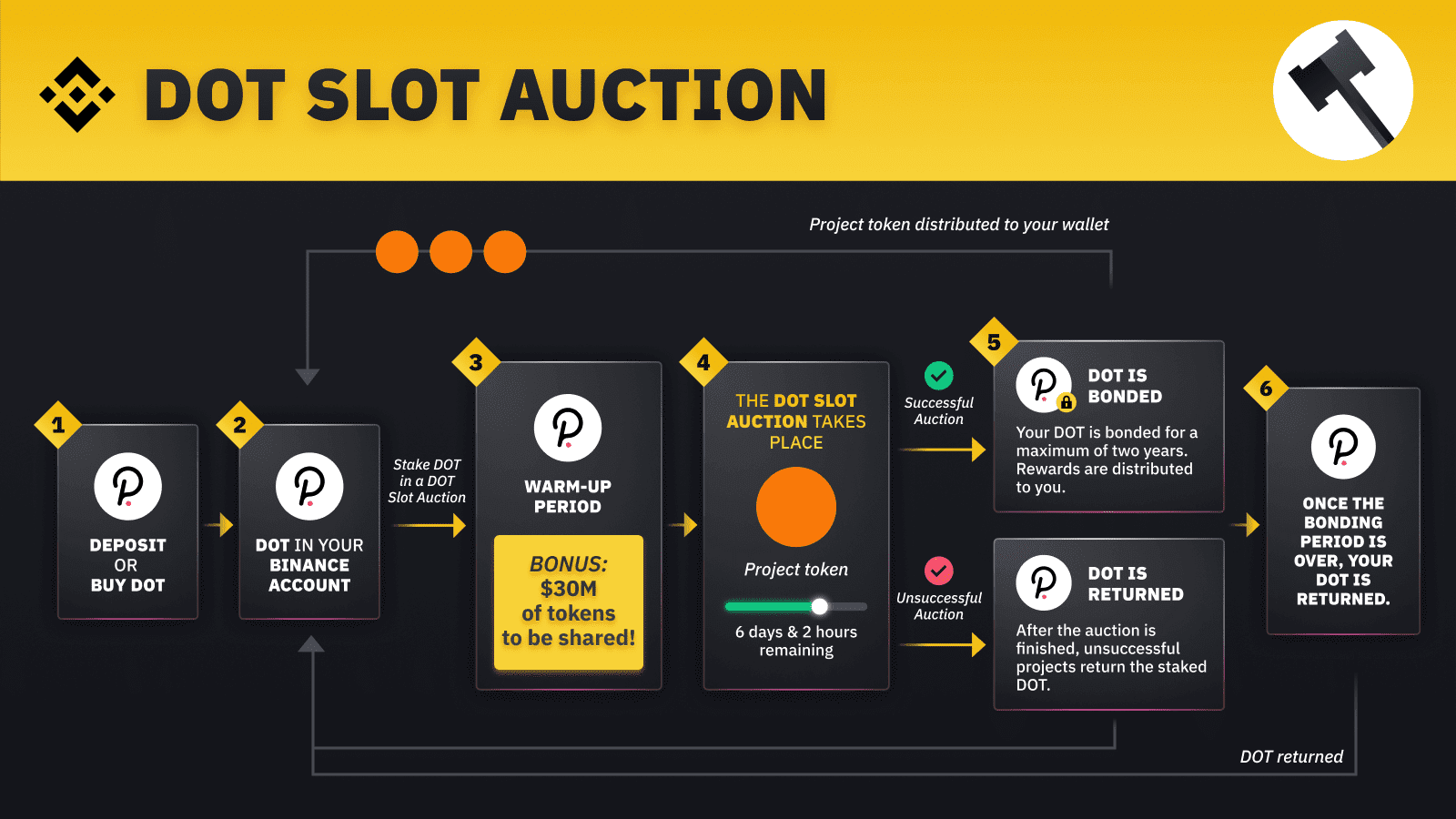
Polkadot takes blockchain interoperability further with its parachain model. Parachains are specialized blockchains connected to Polkadot’s central Relay Chain, allowing seamless data and asset transfers.
Parachain slots are allocated via auctions, where projects bid DOT tokens for leases. Winners bond tokens for security, and crowdloans let users contribute DOT in exchange for project rewards.
This system fosters competition and innovation, enabling altcoins to connect without building from scratch. For altcoins, it means reduced silos, enhanced scalability, and broader ecosystem participation—potentially boosting their value through network effects.
How to Earn Interest on Polkadot (DOT) with Parachain Slot …
This diagram outlines the parachain auction process, showing how bids secure slots.
Current Trends and Real-World Relevance
Blockchain extends beyond crypto into supply chain tracking, voting systems, and healthcare records. In fintech, DeFi platforms have grown to manage billions in assets.
A key data-backed insight: By 2025, over 1 billion people are estimated to use blockchain wallets, up from 81 million in 2020, driven by mobile adoption in emerging markets.
Trends like Web3 emphasize user-owned data, while regulatory developments, such as clearer U.S. guidelines, influence market stability.
For visual learners, embed this educational video on blockchain basics: How Does a Blockchain Work – Simply Explained.
Pros, Risks, and Common Misconceptions
Blockchain’s advantages include transparency, reducing fraud through public ledgers, and efficiency by cutting intermediaries.
However, risks abound: Price volatility can wipe out investments overnight, and scalability issues like network congestion persist. Environmental concerns with PoW add another layer.
A common misconception is that blockchain equals anonymity—transactions are pseudonymous but traceable. Another is viewing it solely as a get-rich-quick scheme; its true value lies in utility.
Actionable Insights for Newcomers
Start by educating yourself through reputable sources like CoinDesk or IBM’s blockchain resources. Set up a secure wallet and experiment with small transactions.
Watch for trends like layer-2 solutions for faster processing or integrations with AI. Consider diversifying into altcoins like XRP for specific use cases, but always research thoroughly.
Track metrics via platforms like TradingView for charts and analyses.
Conclusion: Embracing Blockchain’s Long-Term Potential
Blockchain, from Bitcoin’s inception to altcoins like XRP and innovations like Polkadot’s parachains, represents a shift toward decentralized systems. While challenges remain, its ability to foster trust and efficiency positions it as a cornerstone of future finance.
As blockchain continues to evolve, how might it redefine your role in the global economy?
(Note: This is not financial advice. Crypto is volatile; always DYOR and only invest what you can afford to lose.)
References
- For more on consensus: Consensus Mechanisms Guide
- Smart contracts details: Investopedia on Smart Contracts
- Polkadot auctions: Moonbeam Network Explanation